Lead halide perovskites open great prospects for optoelectronics and a wealth of potential applications in quantum optical and spin-based technologies. Precise knowledge of the fundamental optical and spin properties of chargecarrier complexes at the origin of their luminescence is crucial in view of the development of these applications. On nearly bulk Cesium-Lead-Bromide single perovskite nanocrystals, which are the test bench materials for nextgeneration devices as well as theoreticalmodeling, we performlow temperature magneto-optical spectroscopy to reveal their entire band-edge exciton fine structure and charge-complex binding energies. We demonstrate that the ground exciton state is dark and lays several millielectronvolts below the lowest bright exciton sublevels, which settles the debate on the bright-dark exciton level ordering in these materials. More importantly, combining these results with spectroscopic measurements on various perovskite nanocrystal compounds, we show evidence for universal scaling laws relating the exciton fine structure splitting, the trion and biexciton binding energies to the bandedge exciton energy in lead-halide perovskite nanostructures, regardless of their chemical composition. These scaling laws solely based on quantum confinement effects and dimensionless energies offer a general predictive picture for the interaction energies within charge-carrier complexes photogenerated in these emerging semiconductor nanostructures.
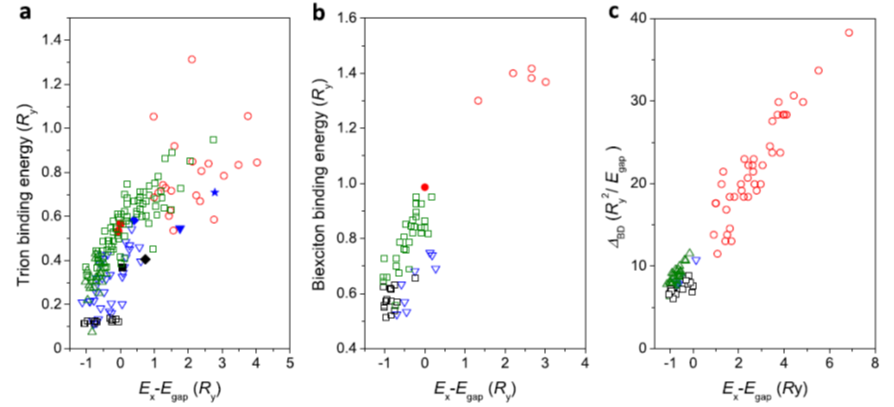
Scaling laws of charge-complex energies in lead-halide perovskite single NCs. Evolutions of the single-NC trion binding energies in Ry units (a), biexciton binding energies in Ry units (b) and dark-bright exciton energy splittings in Ry2/Egap units (c) as a function of the exciton recombination energy expressed in Ry units after bandgap subtraction.
Article published in: Nature Communications