Sommaire
Presentation
Fiber optics offers a multitude of possibilities in terms of sensors. Indeed, the implementation of very long optical paths allows high measurement sensitivity. Furthermore, the fiber itself is a very sensitive sensor to different physical parameters (temperature, mechanical or chemical constraints, etc.). In the DOP team, we develop original fiber architectures allowing us to measure very weak effects.
Fiber Sagnac interferometer
The fibered Sagnac interferometer is an instrument allowing access to the measurement of non-reciprocal effects, i.e. a dependence of the optical index with the direction of travel of the light in the sample. This passive 2-wave fiber interferometer is inspired by the fiber gyroscope used to measure the Sagnac effect. Our instrument thus makes it possible to measure small or poorly understood physical effects.
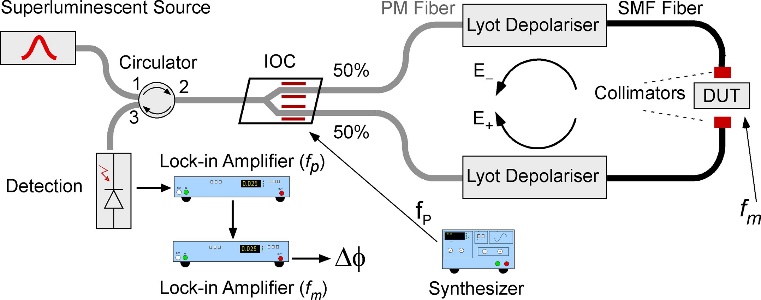
Measurement of magnetochiral birefringence
The magnetochiral interaction results, in the optical domain, in a difference in absorption coefficients and refractive indices associated with two counter-propagating waves in a chiral medium subjected to a longitudinal magnetic field. Observations of magnetochirality in optics are rare, the effect being small. The contribution to absorption, called magnetochiral dichroism, was observed for the first time in 1998. We have developed fibered and depolarized Sagnac interferometers at 1.5µm and 0.8µm, presenting a detection floor below 500 nrad.Hz-½, for the detection of the magnetochiral index of molecules in solution.


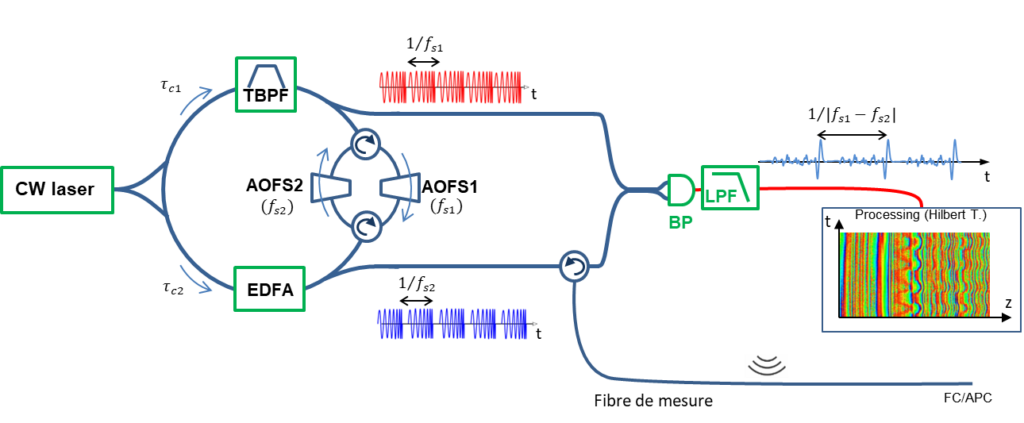
Distributed acoustic sensing (DAS)
We have implemented a fiber interrogator, capable of measuring in real time the index profile along a fiber with sub-cm resolution. The system is based on the principle of multi-heterodyne or dual-comb interferometry. The dual-comb source is a bi-directional frequency-shifting loop, which delivers several hundred mutually coherent teeth. The spatial and temporal resolutions of the technique are respectively a few mm and a few tens of µs. This interrogator should make it possible to measure the wall pressure in aero or hydrodynamic flows around moving solids.
Financial support
- CNRS (Programme défi instrumentation aux limites 2015)
- ANR (project COCOA, project MECHOUI)
Research staff involved
Research engineers, researchers and professors
-

LOAS Goulc’hen
(+33)2 23 23 68 81 Research Engineer
-

ALOUINI Mehdi
(+33)2 23 23 66 58 Professor Directeur d’Unité
-

VALLET Marc
(+33)2 23 23 62 04 Professor Responsable de département
-

GUILLET DE CHATELLUS Hugues
(+33)2 23 23 47 29 Senior Researcher
PhD and post-doc
-

ALLIOT DE BORGGRAEF Louis
PhD (09/2022-11/2024)
To know more…
- Goulc’Hen Loas, Mehdi Alouini, Marc Vallet. Optical fiber Sagnac interferometer for sensing scalar directional refraction: Application to magnetochiral birefringence. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2014, 85 (4), pp.043109. ⟨10.1063/1.4871988⟩. ⟨hal-01063260⟩
- Chengshuo Shen, Goulc’Hen Loas, Monika Srebro-Hooper, Nicolas Vanthuyne, Loic Toupet, et al.. Iron Alkynyl Helicenes: Redox-Triggered Chiroptical Tuning in the IR and Near-IR Spectral Regions and Suitable for Telecommunications Applications. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55 (28), pp.8062-8066. ⟨10.1002/anie.201601633⟩. ⟨hal-01318820⟩
- Louis Alliot de Borggraef, Hugues Guillet de Chatellus. Phase-sensitive distributed Rayleigh fiber sensing enabling the real-time monitoring of the refractive index with a sub-cm resolution by all-optical coherent pulse compression. Optics Express, 2023, 31 (2), pp.1167. ⟨10.1364/OE.479006⟩. ⟨hal-04230634⟩